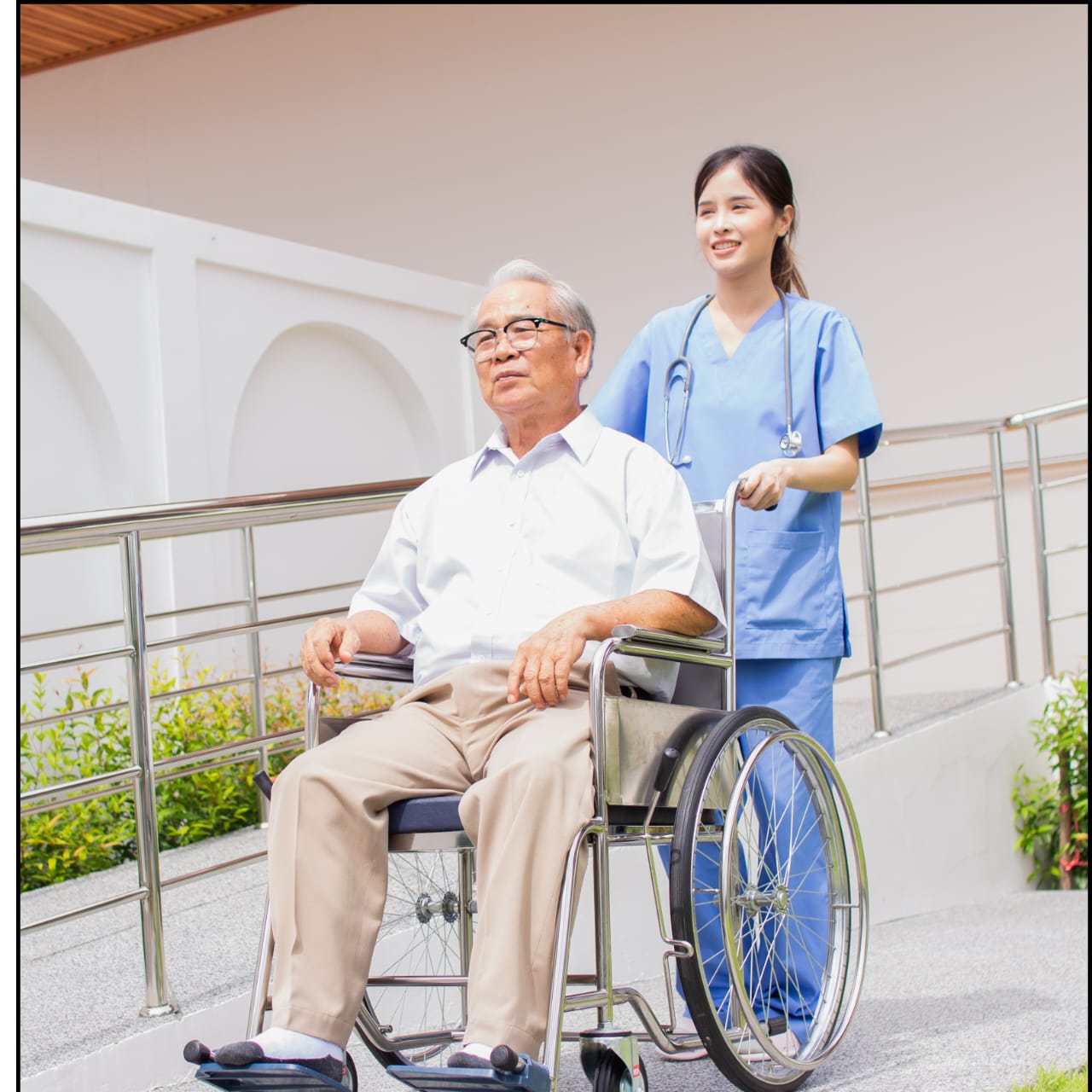
HOME CARE SERVICES :
To Provide a Full range of cost-effective and quality focused home health care services to our clients. we aim to lengthen out history through successful case, management and personalized delivery of healthcare. While Serving as trusted resource for our community.
OUR SERVICE
-
✅ Elder Care
-
✅Nursing Services
-
✅ Personal ICU
-
✅ Short Term Intervention
-
✅ Attendent
-
✅ Physiotheraphy
-
✅ Palliative Care
-
✅ Infant and Mother Care
WHAT IS HOME CARE SERVICES ?
Home care, also known as home health care, refers to medical and non-medical services provided to patients in the comfort of their own homes. The goal of home care is to help individuals recover, rehabilitate, or manage chronic conditions while maintaining their independence and quality of life.
*Types of Home Care:*
1. *Medical Home Care*: Provided by licensed healthcare professionals, such as nurses, therapists, and doctors, to manage medical conditions, including:
- Wound care
- Infusion therapy
- Pain management
- Rehabilitation therapy (physical, occupational, speech)
2. *Non-Medical Home Care*: Focuses on daily living assistance, such as:
- Personal care (bathing, grooming, dressing)
- Meal preparation
- Light housekeeping
- Companionship
- Transportation
*Benefits of Home Care:*
1. *Convenience*: Care is provided in the comfort of the patient's own home.
2. *Personalization*: Care plans are tailored to individual needs and preferences.
3. *Cost-effectiveness*: Often less expensive than hospital or facility-based care.
4. *Improved outcomes*: Patients tend to recover faster and have better health outcomes in the comfort of their own homes.
5. *Increased independence*: Patients can maintain their independence and autonomy.
*Who is Eligible for Home Care?*
1. *Seniors*: Older adults who need assistance with daily living activities or medical care.
2. *Chronically ill*: Individuals with conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or respiratory disease.
3. *Post-surgical patients*: Those recovering from surgery or hospitalization.
4. *Disabled individuals*: People with disabilities or mobility issues.
5. *Terminal patients*: Those requiring end-of-life care or hospice services.